In order to cope up with a world that is completely digitalised, it is essential to move past the realm of textbooks and immerse yourself in working environments led by tech. This enables students to cultivate the skills, knowledge and technical ability to thrive in the real world. Experiential learning has become a necessity in schools. This is where the School Innovation Council or the SIC comes in, a revolutionary initiative taken by the Ministry of Education’s Innovative Cell, leading Indian education towards a more positive direction. The SIC hence plays a crucial role in nurturing young minds into doers rather than thinkers, and thus creates better leaders for tomorrow.
Why is Experiential Learning Crucial for Students of the 21st-Century?
Experiential learning requires students to work on real-life problem solving, allowing them to apply their theoretical expertise in practical scenarios. This method of getting students to do the practical work necessary for the subjects they are studying, helps them get an in-depth understanding of the field they want to pursue their higher studies and career in. This idea of getting hands-on experience aligns with the goals of NEP 2020 and school reforms, which is now being used in increasing classrooms across India.
Key Benefits of Experiential Learning:
- Active Engagement: Students participate actively, rather than passively absorbing knowledge
- Real-World Skills: Problem-solving and critical thinking are emphasized by making the students work on practical tasks.
- Collaboration: Team-based projects teach teamwork, empathy, and better communication – all of which are important in order to lead successfully
- Creativity and Innovation: Students explore innovative new ways to approach challenges, which allows their individual creativity to shine through
How SIC Turns Classrooms into Innovation Hubs
The SIC transforms traditional classrooms into hubs of exploration and creativity by bringing together students and teachers alike to work on and develop solutions to real-world problems. It is SIC’s main objective to ensure that students not only know how to create ideas, but also find ways to implement them in practical real-world scenarios.
SIC’s Innovative Framework:
- Innovation Challenges: Students participate in themed challenges that focus on addressing and solving real-world issues.
- Tinkering Labs: Hands-on spaces where students experiment and execute viable prototype ideas.
- Start-Up Mentorship: Students are mentored by leading entrepreneurs who help turn their ideas into profitable business ventures.
This way, SIC turns classrooms into innovation hubs, fostering creativity, curiosity and experimentation that drive students to take an initiative to bring about a positive change. This transformation not only helps students interact more, it also builds an environment that drives innovative minds.
Project-Based Learning Models Introduced by SIC
SICs initiative revolves around project-based learning, where students are required to work on important complex tasks over extended periods of time. These projects are not limited to their academic curriculum, they expose to students the real world problems people around them face, and encourage them to find solutions for these problems.
Types of SIC Projects:
- Eco-friendly Solutions: Projects like building sustainable school infrastructure or designing energy-efficient devices.
- Social Impact Projects: Addressing issues like sanitation, water conservation, and education.
- Tech Development: Students create mobile apps or digital solutions to improve daily life.
These student-led innovation projects through SIC are more than just assignments, they are acts of service towards bettering the communities around them. Projects like these teach students the importance of conducting proper research, draft solutions, get feedback from the people around them and refine their ideas in order to match the situation better.
Initiatives Taken by SIC Beyond Projects
SIC is more than just a framework, it is a movement that is built on initiatives aimed at strategically fostering change. SIC has taken initiatives that go beyond classroom projects, some of which are:
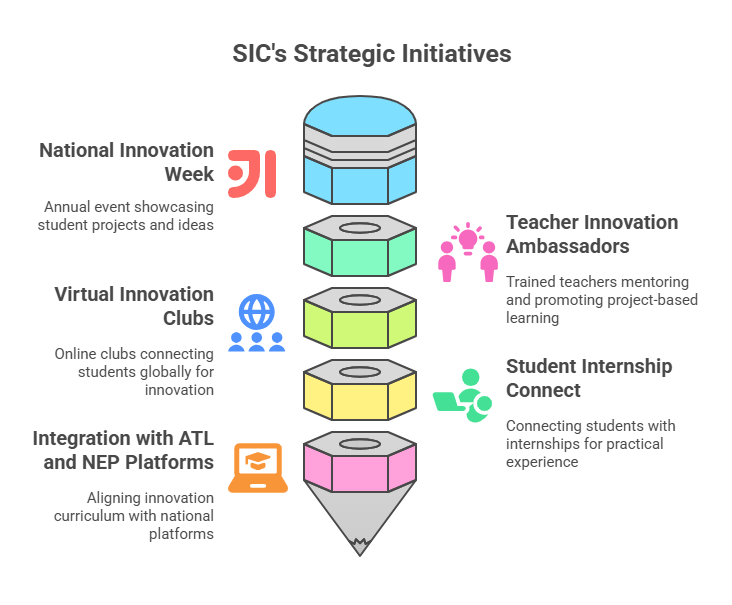
1. National Innovation Week
An annual celebration where schools organize exhibitions, showcase ideas and host pitching competitions.
Students present their projects to community leaders, parents, and industry experts, and refine their projects to better suit what is asked of them based on the feedback they get from these leaders.
2. Teacher Innovation Ambassadors
Teachers who volunteer are required to go through rigorous training and only a few of them become Innovation Ambassadors of their respective districts.
They mentor other educators, organize bootcamps, and encourage project-based learning practices.
3. Virtual Innovation Clubs
Schools without physical infrastructure for tinkering labs can still participate in SIC by organizing innovation clubs online.
These clubs host webinars, mentorship sessions, and virtual collaboration projects that connect students across the globe.
4. Student Internship Connect
SIC works to connect students with local startups, businesses, and social enterprises for short-term internships.
Students benefit from this by gaining hands-on exposure to real work environments, helping them apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios.
5. Integration with ATL and NEP Platforms
Schools with Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL) align their innovation curriculum with SIC’s framework in order to work towards fostering project-based learning.
SIC also integrates NEP 2020’s goals into action plans, ensuring its ideas reach classrooms effectively.
These initiatives showcase SIC’s role in empowering students with experiential learning that go well beyond the walls of a classroom. SIC is successfully reaching an increasing number of institutions, making sure that innovation becomes a prioritized aspect of education.
Success Stories: Students Creating Real-World Solutions
SIC is producing powerful instances of student-impact all across India. Some of which are in:
1. Gujarat – “Food Bridge” App to Tackle Hunger and Waste
Objective:
- The goal was to reduce food waste while also addressing hunger in their local community. The objective was to create a sustainable solution for redistributing surplus food to people in need.
Implementation:
- A team of students from a government school in Ahmedabad built the Food Bridge app using mobile app development platforms. They worked with local food vendors, canteens, and Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) to integrate the app with their systems, in order to execute food deliveries in real time.Organisations were able to contribute food using the app and provide expected pickup times, allowing NGOs to access the supplies.
Impact:
- In the first two weeks of its release, the app redistributed more than 150 meals, helping many less fortunate families. The project raised awareness about food waste and inspired other schools to take action against the same.
2. Odisha – “VoiceBoard” to help Visually Impaired Students
Objective:
- The main objective was to help visually impaired students to access classroom notes and visual content by creating a device that reads written material aloud after scanning it.
Implementation:
- A group of young people from Bhubaneswar developed a device using optical character recognition (OCR) technology and simple Arduino programming. Students with visual impairments can follow classes more easily thanks to the VoiceBoard, which reads aloud content scanned from classroom whiteboards. The device improved accessibility in the classroom and allowed visually impaired students to engage more effectively with their peers. The project received support from local education authorities, who could recognise that scaling it to other schools who work with visually impaired students would teach others to also take the initiative to extend a helping hand to those in need.
Impact:
- The VoiceBoard has significantly enhanced classroom inclusivity for visually impaired students in Bhubaneswar. It enabled these students to independently access real-time visual content, such as whiteboard notes, which were previously inaccessible without assistance. Teachers observed increased participation and confidence among students using the device. The project not only improved academic performance but also fostered a sense of autonomy and dignity. Encouraged by its success, local education authorities are now exploring possibilities for district-wide implementation, positioning VoiceBoard as a scalable, low-cost assistive technology model for inclusive education across Odisha and beyond.
3. Tamil Nadu – Solar Lanterns for Villages that have little to no electricity
Objective:
- The students primary objective was to provide a sustainable solution to power shortages in their village. This was an especially important initiative to take as there is an increasing number of load sheddings in villages during the monsoon season, as they do not have the infrastructure to safely have electricity during a thunderstorm.
Implementation:
- Using simple electrical components like solar panels, plastic bottles, and LEDs, students from a school close to Tirunelveli created and constructed solar lanterns.To make sure the design could be readily implemented in low-income households, they tested the lanterns in their village and school using inexpensive materials. In order to replicate the initiative in their own homes, the students also produced instruction manuals for the villagers.
Impact:
- By successfully producing and distributing more than 25 solar lanterns, the project improved households’ quality of life during blackouts, particularly during thunderstorms and periods of intense precipitation. The lanterns became a safer and more sustainable source of light for households, compared to kerosene lamps, which had been their only option before.
These are just a few of the initiatives taken by the students out of countless others across India. They teach real-world skill development, showing that young people—when given the right tools and encouragement—can work through even the most complicated challenges.
Such experiences foster not just technical knowledge, but also empathy towards others and to look beyond just one’s personal needs and goals. They show students that their ideas matter, their voices count, and their actions can lead the world to a better tomorrow.
Training Teachers to Guide Experiential Learning
Even though fostering innovation in students is the main objective of the SIC, its success largely depends on teachers who are equipped with the required knowledge to guide the students. SIC believes that teachers should not just teach academics, but also organize projects that help students work on their personal creativity, helping them innovate ideas successfully.
How do they achieve it?
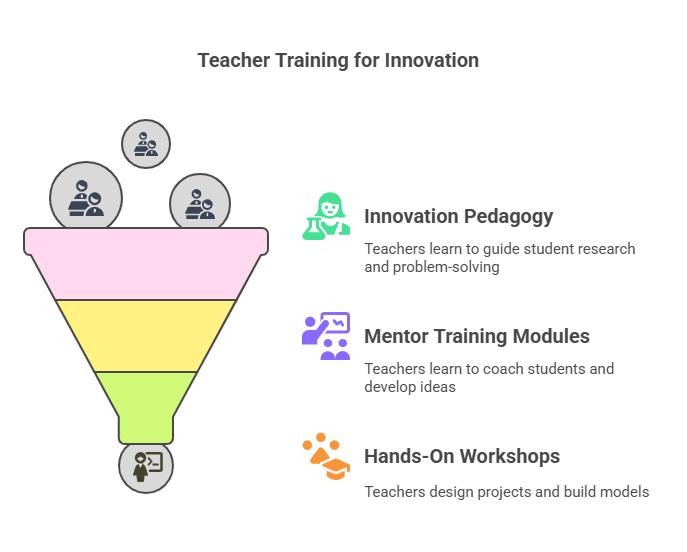
- Innovation Pedagogy: SIC organizes workshops, webinars and official training sessions for teachers to understand topics like guiding student research, problem solving, using prototype tools and technology like Arduino and Scratch.
- Mentor Training Modules: These are specialised training courses that show teachers how to guide students through the process of innovation. It teaches methods to improve experiential learning, how to coach students on developing profitable ideas and how to present them in order to encourage project-based learning.
- Hands-On Workshops: Some SIC organisations have training laboratories where teachers participate in activities that require them to work hands-on. They design sample projects, build working models and experiment with new and practical teaching environments
These trained educators, who are specifically required to work in a way that fosters innovative creativity, are a crucial component of SIC’s initiative to empower students with experiential learning.
Experiential Learning in Line with NEP 2020
The National Education Policy 2020 marked a major transformation in Indian education by implementing student-friendly and skill based learning methods. It deeply resonates with the values that are incorporated in the SIC framework.
NEP 2020 & SIC Alignment:
- Competency-Based Learning:There is a huge focus on developing real-world skills and not just limiting the students to academic knowledge. Academics is the base of education, but it does not stop there. It is very important to learn skills that are needed in practical scenarios in order to secure your dream profession.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Using creative projects to promote multidisciplinary learning.
- Vocational Exposure: In addition to academic disciplines, schools offer career-oriented learning.
SIC ensures that innovation is ingrained in the school’s culture rather than being used sometimes by coordinating experiential learning with NEP 2020. Through this, schools not only comply with national education standards, but also offer an experience, which helps students prepare for the future.
Role of SIC in Fostering Entrepreneurship in Students
Innovation doesn’t end at ideas, it needs to be further transformed into solutions, ventures and movements. That’s why SIC strongly focuses on entrepreneurship. Students are introduced to the basics of business, market research, financial planning and pitching through bootcamps and innovation festivals.
Entrepreneurial Skills Taught
- Business Planning: Understanding how to take an idea from concept, and turning it into a practical, market ready plan
- Pitching: Developing good public speaking and presentation skills to pitch ideas to investors or the community.
- Financial Literacy: Teaching students how to manage budgets and investments.
These exposures highlight the role of SIC in fostering entrepreneurship in students, encouraging them to think beyond just thinking about innovation and towards impact. Whether they dream of launching a start-up, or becoming an industrialist, students are supported every step of the way.
A National Movement for Student Innovation
As more schools across India adopt SIC, it is rapidly becoming a national movement. This shift is opening up access to innovation and providing opportunities for students from all backgrounds. Students from rural, urban, government, and private schools are all finding their place in the real world. The vibrant community of SIC India is playing a key role in empowering these students.
SIC’s National Impact
- Innovation Challenges: National level competitions that connect students from across the country.
- Collaborative Platforms: An educational platform where students share ideas and learn from their peers in different regions.
- Cross-School Partnerships: Schools work together on projects, leading to the exchange of knowledge.
By promoting SIC’s online discussion boards, interschool contests, and innovation challenges, a shared space for development is created. School administrators, educators, education reformers, and student mentors are driving this movement because they understand that transforming education today is necessary to prepare students for the future.
From Learners to Leaders
Students are being empowered through the School Innovation Council, often known as the SIC, in addition to receiving instruction. They are being forced to exercise critical thinking, bravery, and daring innovation.
From designing solar lamps to launching apps that help those who don’t have anyone to organizing awareness campaigns, young innovators of India are proving that age is no barrier to create effect.
It’s time to reframe educational achievement in terms of our students’ creativity and curiosity instead of just focusing on their exam scores. Our students are our future, after all. Let’s help them do better.
References:
- Ministry of Education, Government of India. (n.d.). School Innovation Council (SIC). Retrieved from https://mic.gov.in/sic
- National Education Policy 2020. (2020). Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India. Retrieved from https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/NEP_Final_English_0.pdf
- Atal Innovation Mission – NITI Aayog. (n.d.). Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL). Retrieved from https://aim.gov.in/atl.php
- CBSE Academic. (2023). Implementation of Experiential Learning and Competency-Based Education. Central Board of Secondary Education. Retrieved from https://cbseacademic.nic.in
- UNESCO. (2021). Reimagining our futures together: A new social contract for education. Retrieved from https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000379707
- NITI Aayog. (2021). School Education Quality Index (SEQI). Retrieved from https://www.niti.gov.in/school-education-quality-index
- India Today. (2023, October 12). How School Innovation Councils Are Cultivating Entrepreneurial Mindsets. Retrieved from https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/featurephilia/story/school-innovation-councils-cultivating-entrepreneurial-mindsets-2448936-2023-10-12
Written by Manjul Kathotia.
